In the realm of visuals, color printing plays a pivotal role in our ability to communicate clearly and effectively. With its vast potential to amplify the essence of images and text, understanding the mechanics and mastery of color printing is imperative for professionals across various fields.
This comprehensive guide unravels key aspects of color printing, starting from the basic understanding of different color printer types and their respective functionings to the enriched complexities of color management. In addition, we delve into hands-on practice to transfer theoretical knowledge derived into tangible skills.
This page covers
Types of color printers: Inkjet, Laser, and Dye-sublimation
One of the important aspects of understanding color printing is knowing the different types of printers. The most common types include inkjet, laser, and dye-sublimation printers.
Inkjet printers
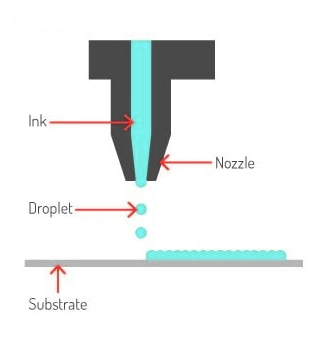
Inkjet printers are versatile printers that work by spraying droplets of ink onto the paper. This results in high-resolution images and offers a wide spectrum of colors, making them ideal for printing photos, professional presentations, and colorful graphics. Besides, they are relatively inexpensive and small in size, making them suitable for home and small business use.
Inkjet printers are preferred by users who need excellent quality and precision printing, especially those dealing with images and photographs. Inkjets can print at higher resolutions with excellent precision.
Laser printers
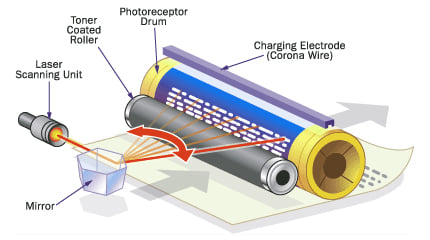
As illustrated in the image above, a laser printer uses a laser beam to produce an image on a drum. The image attracts a toner powder that is then transferred onto paper.
Laser printers offer faster printing speed and are capable of handling large print jobs. They are best suited for text-heavy documents, but high-end color laser printers can also produce excellent color images. Laser printers are ideal for all business sizes, as well as personal use, but are mostly used for speedy printing jobs.
Dye-sublimation printers
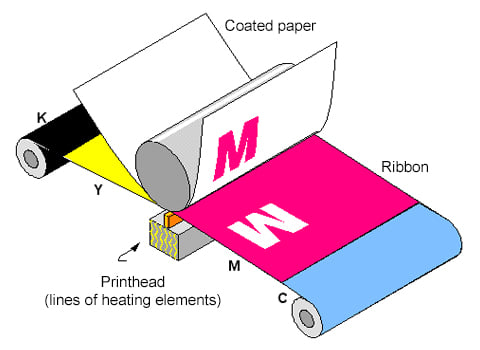
Dye-sublimation printers operate using a heating process to transfer dye to a medium such as a plastic card, paper, or fabric. They are unique in the fact that they use a ribbon with panels of color (CMYK) rather than individual cartridges for different colors. This allows for a higher range of colors and shades, delivering higher-quality photographic prints with smoother gradation.
However, dye-sublimation printers are typically more expensive and slower in printing speed, making them unsuitable for text-heavy printing.
What type of printer to use?
Assessing print quality
Print quality depends largely on the printer type and the printing technique. For example, both Inkjet and high-end laser printers can deliver sharp, vibrant-colored, high-resolution prints ideal for photos or graphics-heavy documents.
However, dye-sublimation printers, exceeding both inkjet and laser, are the preferred choice where premium print quality is needed, especially for professional photographs and high-quality artwork.
Determining ideal usage
The ideal usage of each printer depends on your requirements. If you need to print photos or other high-resolution images, an inkjet or dye-sublimation printer would be a good choice. For regular printing needs with mostly text or simple graphics, a laser printer provides the fastest and most cost-effective solution.
When printing professional-level photographs or high-end brochures and marketing materials, you might want to consider a dye-sublimation printer for its superior color blending and detail reproduction.
By understanding the basics of each type of color printer, their functioning, the quality of the print they produce, and the ideal usage, you’ll be equipped to make an informed choice about the most suitable printer for your needs. Always consider the print quality, speed, cost, and specific requirements of your print job.
Color Management in printing
Color management is a crucial aspect of any color printing process. It involves controlling how colors will appear on the printed product and handling different color data between devices like monitors, scanners, and printers.
The aim of color management is to achieve consistency and accuracy of colors from the source to the final output.
Printer drivers and color profiles
Printer drivers and color profiles significantly influence the quality of your print. The printer driver translates the data from your computer to the printer. It commands the printer how to print the data, including the information about the color.
Color profiles, on the other hand, assist in ensuring the colors appear the same across different devices. Utilizing the right profile for your printer can drastically enhance the fidelity of the colors in your print.
Printer and monitor calibration
To achieve accurate color output, you must calibrate your printer and monitor. Each device can display or print a different range of colors. For consistency, it is essential to adjust or ‘calibrate’ them. Calibration ensures that what is displayed on the monitor is what will be printed.
There are tools available, such as colorimeters or spectrophotometers, that can assist with the calibration procedure.
Understanding CMYK and RGB color models
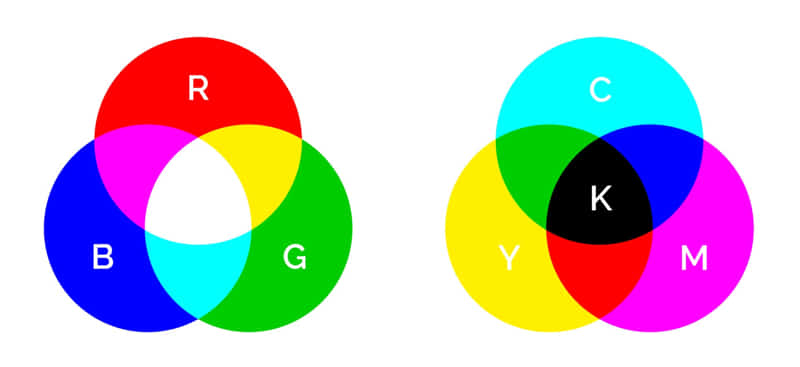
The CMYK and RGB color models play a vital role in print quality. CMYK, standing for “Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black),” is typically used in the printing process. On the other hand, RGB, representing “Red, Green, and Blue,” is used for digital displays.
When creating an artwork intended for printing, it’s crucial to use the CMYK color space. This is because the RGB color model has a wider range of colors that cannot always be accurately reproduced with CMYK.
Significance of CMYK and RGB in printing
When an RGB image is printed, the printer must convert the RGB colors into CMYK. Sometimes during this conversion, colors can slightly change because the CMYK color gamut is narrower than RGB. Therefore, for more accurate color matching and better print quality, it is preferable to work in the same color space that the printed output will be in – for most color print jobs, this will be CMYK.
Hands-on with color printers
This section gives a step-by-step of the process that you must go through in order to successfully get a colored print from your printer.
-
Check for color printing capability
In order to print in color, the first step is to ensure that your printer has the capability to do so. Check your printer’s settings and make sure that it is set to print in color. This can typically be found by accessing your printer’s preferences menu and looking under the “printing” or “print quality” section.
If your printer does not have a color setting, it may not be capable of color printing.
-
Select a document to print
Start by selecting a document or photo that contains colored graphics. This will provide better visibility for changes in color print quality. Also, make sure the file format is compatible with your printer model.
-
Open the Print menu
Open the file you have chosen to print. Go to “File” in the ribbon menu and select the “Print” option. Before hitting the “Print” button, carefully look through the print dialog box to make sure you’re utilizing your desired settings.
Alternatively, you can also press the CTRL + P shortcut keys to open the Print menu.
Open the Print menu -
Select color printing
In the print dialog box, there will be an option to print in grayscale or in color. Select the color option.
If the option to print in color appears grayed out or non-selectable, this might indicate an issue with the color cartridge, or a printer malfunction.
-
Experimenting with color settings
Experiment with different color settings to find what works best for printed materials. The “high quality” setting usually uses more ink, but it often results in brighter, more vibrant colors.
Try different quality settings with varying image complexities to get a sense of how your printer performs under different settings.
-
Monitor results and troubleshoot
Observe the outcome of your color prints. Look for any color inconsistencies or printing issues. If you encounter any issues, troubleshoot the problem based on your printer’s user manual or manufacturer’s online resources.
-
Performing regular maintenance
Perform regular maintenance on your printer to keep the color prints at a high quality. This might include cleaning the print heads and calibrating the printer for color accuracy. Always have spare color cartridges ready for replacement when needed.
Through hands-on practice, trial, and error, you will become familiar with the intricacies of color printing and improve your ability to troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Ending words
Having journeyed through the in-depth analysis and practical application of color printing, you are now equipped with a holistic understanding of this domain. We have navigated from grasping primary concepts around varied printer types, their operational mechanisms, and suitable applications to the pervasive importance of color management.
Through hands-on practice, theoretical concepts have been translated into practical skills, fortifying your learning experience. The path to mastering color printing doesn’t end here. It’s a continuous process of exploring, experimenting, and learning through experiences. Let the vibrant world of color printing open up new dimensions for you, enhancing your ability to communicate visually in the most effective ways.





