Over the years, printing technology has advanced beyond our imagination, and users can now print their favorite designs on any material. However, the technique will vary, and that’s how various printing types were discovered.
With the difference in techniques, there also comes a notable difference in the quality. The choice of a specific printing type depends on the purpose of use, printing material, and desired quality.
Following are the different printing types and techniques people use to create eye-popping crafts.
Table of Contents
Traditional Printing Techniques
Woodblock Printing

It is the oldest method used for printing and is now overtaken by newer techniques. This traditional method involved carving an image or text onto a wood block. Then that block was used to make ink impressions on paper, fabric, or other materials.
Woodblock prints could last hundreds of years if properly cared for, making them a durable form of printmaking. It was one of the most versatile printing types used to print fine art, illustrations, text, and other designs.
This printing technique is important to many cultural traditions, particularly in East Asia. Some underdeveloped areas in this region still follow this method.
Pros
- Relatively simple and cost-effective.
- Allows to produce multiples of the same color, image, or text.
- The blocks can be reused multiple times.
Cons
- It is a labor-intensive process, as each block must be carved by hand.
- The blocks are fragile and can be easily damaged.
- Unsuitable for printing large volumes.
- Only one color can be printed at a time, making it difficult to produce multi-colored images or text.
Engraving

Engraving printing is another traditional method that is still widely used. It requires an engraved plate to transfer an image or text onto paper or other materials. The plate is typically made of metal, such as copper or steel.
The image or text is engraved into the plate using a sharp tool by hand. The ink is then filled into the engraved design. The entire process results in crisp images and a somewhat 3D look.
Not only is this technique time-consuming, but also one of the priciest among all printing types. This method is widely used for printing top-end business cards for high officials or royal invitation cards.
Pros
- Produces high-quality, detailed images and text.
- Allows the use of multiple colors in a single print.
- Well-suited for printing banknotes, invitation cards, and other high-value items.
Cons
- Time-consuming.
- Expensive compared to other printing methods.
Litho Printing
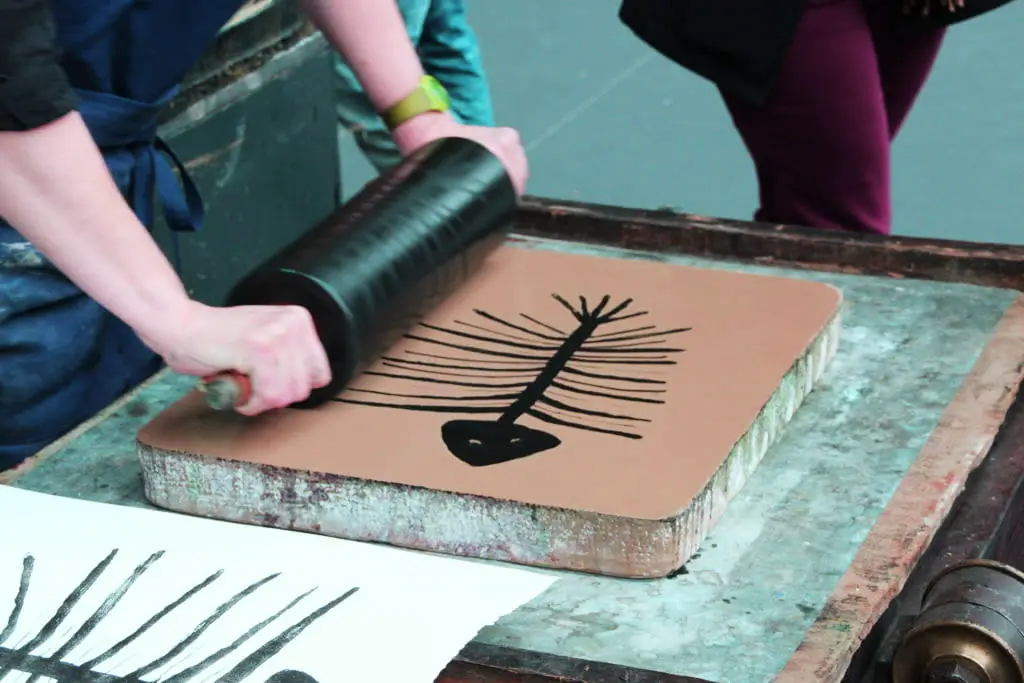

Lithography, also known as litho printing, uses a flat stone or metal plate on which the image or text to be printed is drawn or etched. It dates back to the 17th century when lithography was initially used for maps and musical scores.
The plate is then treated so that the areas to be printed are ink-receptive, and the non-printing areas are ink-repellent. A roller then applies ink to the plate, which is then transferred to a sheet of paper or other material under pressure.
The process is efficient for medium and long runs, with the capability of producing thousands of copies, and is capable of reproducing fine details and a wide range of colors. It is best used for commercial printing, stationary and fine arts printing, fabric, mugs, billboards, and more.
It’s worth noting that lithography printing is unsuitable for very small runs, as the cost of creating the plates is relatively high. But it’s still considered a high-quality printing method, especially for printing on paper.
Pros
- Highly versatile method.
- Pretty affordable compared to other traditional techniques.
- Produces brilliant designs with vibrancy and clarity.
Cons
- The procedure is complex.
- The use of chemicals and solvents can harm the environment
- Requires a high level of skill and expertise to operate the machinery.
Modern Printing Techniques
Digital Printing
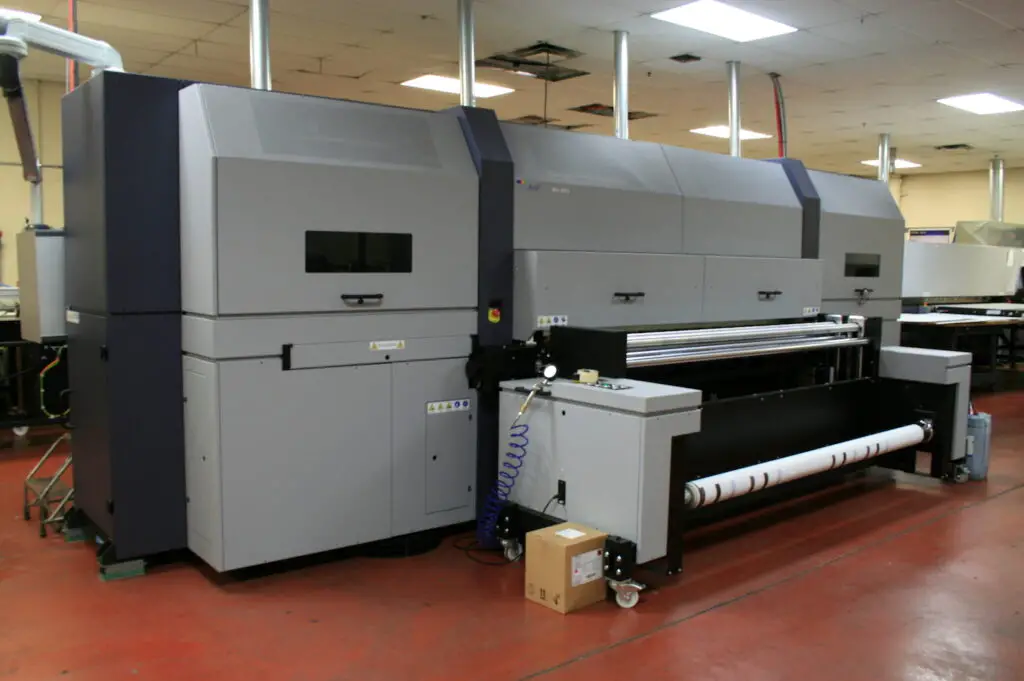

It is the most commonly used printing technique. Unlike old printing types, in this method, digital files are sent directly to an electronic printer without needing a physical stencil or plate.
A digital printer uses a digital file, such as a PDF or image, as the source for the print job. The file is sent to the printer, which is processed by the printer’s software. The printer then uses a series of electronic devices, such as laser beams or inkjet heads, to apply the ink or toner to the paper or other media.
The printer then uses a series of tiny nozzles or a laser to apply the ink or toner to the paper.
There are two types of digital printers, i.e., Inkjet printers and Laser printers.
- Inkjet printers – These feature ink cartridges filled with inks of different colors. Tiny droplets of these inks are sprayed onto the paper to create the image.
- Laser printers – In these printers, toner cartridges are used. The laser beam heats the powdered toner, which melts and sticks to the paper to print the design.
Digital printing is often used for short runs of printed materials, such as brochures, business cards, and posters, and for printing personalized items, such as invitations and photo prints.
Pros
- Ideal for producing copies in less time.
- It offers a great degree of personalization.
- Produces exceptionally appealing designs with sharp details and colors.
Cons
- Expensive for large runs of printed materials.
- Some digital printers are limited in the types of paper they can print on.
- Requires regular maintenance and replacement of parts, which can be costly.
3D Printing
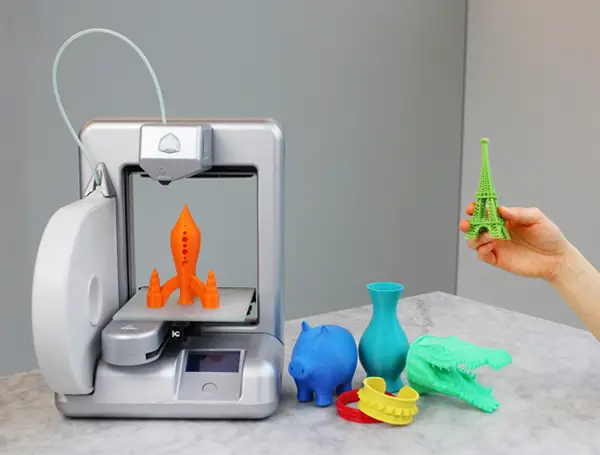

As the name suggests, this technique involves turning your desired digital design into a three-dimensional object. It is also known as additive manufacturing.
There are size limitations. Generally, people use these to create small toy figures, promotional freebies, display objects, etc.
Technology is evolving, and more materials are being developed that can be used for 3D printing, which will greatly expand the range of objects that can be created. It’s a versatile technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way things are made.
A 3D printer reads a digital file, such as an STL file, and creates a three-dimensional object by adding successive layers of material, such as plastic, metal, or ceramic.
There are several different types of 3D printing technologies. Some of the most common types include:
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
This is the most common type of 3D printing and works by heating a plastic filament. The melted material is then extruded through a small nozzle to create the object.
-
Stereolithography (SLA):
This type of 3D printing uses a laser to cure a liquid resin, layer by layer until the object is complete.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
SLS uses a laser to sinter, or melt, a powdered material, such as plastic or metal, layer by layer and creates the desired object.
-
Binder Jetting:
This method involves a liquid binder selectively deposited onto a powder bed to produce the object.
-
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF):
MJF is a process that uses a combination of heat, pressure, and fusing agents to fuse the plastic powder layers together.
3D printing is popular in many industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and manufacturing. It’s used to create everything from simple prototypes to complex, functional parts, including aerospace components, medical implants and prosthetics, and even entire buildings.
Wonder what else is left to see in the future!
Pros
- Able to create complex designs.
- Reduces material waste and cost.
- Not very time-consuming.
- Highly versatile.
Cons
- Objects produced might not be of the best quality.
- Size limitations.
- Objects require additional post-processing for surface finish.
- Expensive for larger runs.
- Requires special handling.
Offset Lithography

It is a modern version of the standard lithography that is best used for professionally creating magazines, newspapers, brochures, etc. This technique is also suitable for printing textbooks. Rightly so, these are exceptional when it comes to large print runs.
It uses a similar process as lithography but with an offset press that uses a rubber blanket to transfer the ink from the plate to the paper. This method is more efficient for medium and long runs, with the capability of producing thousands of copies.
Pros
- High-quality and speedy prints.
- Ideal for large runs.
- Compatible with a variety of printing materials.
Cons
- Expensive and tedious setup.
- Demands frequent maintenance.
- Only skilled people can operate the machinery.
Screen Printing

This technique is among the old methods but is still widely used for professional printing purposes. Initially, the application was confined to the silk fabric only. Over time, this technique has become an extremely versatile method that can be used to print on various surfaces, including paper, fabric, glass, metal, and ceramics.
Screen printing is suitable for small or large runs and can print a wide range of designs and images with high accuracy. However, it can be time-consuming and labor-intensive compared to other printing methods.
Pros
- The prints produced possess excellent durability and don’t fade.
- Works well for small and large runs.
- Cost-effective for bulk printing.
Cons
- Specialized setup required.
- Limited stencil and color options.
- Labor intensive.
- Time-consuming.
Embossing
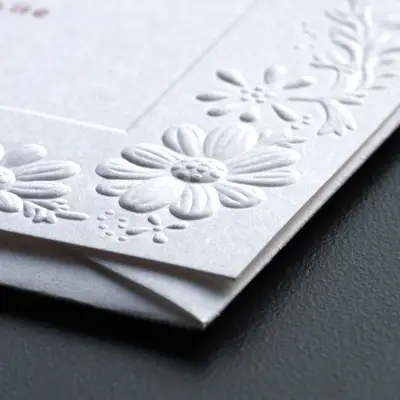

When it comes to producing luxurious prints, the embossing technique comes as a foremost choice. It adds a tactile element to printed materials, making them more interesting and memorable.
This process creates a raised or three-dimensional image on a surface by pressing an image-bearing plate onto the surface. The plate is typically made of metal or plastic and has the image carved into it in relief, meaning that the design protrudes from the plate.
When the plate is pressed onto the surface, the design is transferred onto the surface in a raised or 3D format.
Embossing can be done on a variety of materials, including paper, cardstock, and certain types of fabrics. It can be used for a wide range of applications, such as business cards, invitations, book covers, and packaging. It is commonly used for branding, creating a luxurious effect, and adding tactile interest to printed materials.
There are two types of embossing, i.e., blind embossing and foil embossing.
- Blind embossing – It doesn’t include any ink or foil, the design is only visible by the raised image.
- Foil embossing – As the name refers, it includes metallic or pigmented foil. That said, the design is visible by the raised image and the foil color.
Embossing is an elegant and premium printing technique, but it can be costly and time-consuming, especially for large print runs. Additionally, it can be difficult to achieve fine details in the design, and it may not be suitable for all types of materials.
Pros
- Perfect for producing elegant, luxurious, and appealing prints.
- Creates a sense of depth or dimension in a design.
Cons
- Might not print high details on all types of materials.
- Long printing times for larger runs.
- Requires a separate die or plate for each design.
- Not suitable for multi-color printing.
Fabric Printing Techniques
Dye Sublimation Printing
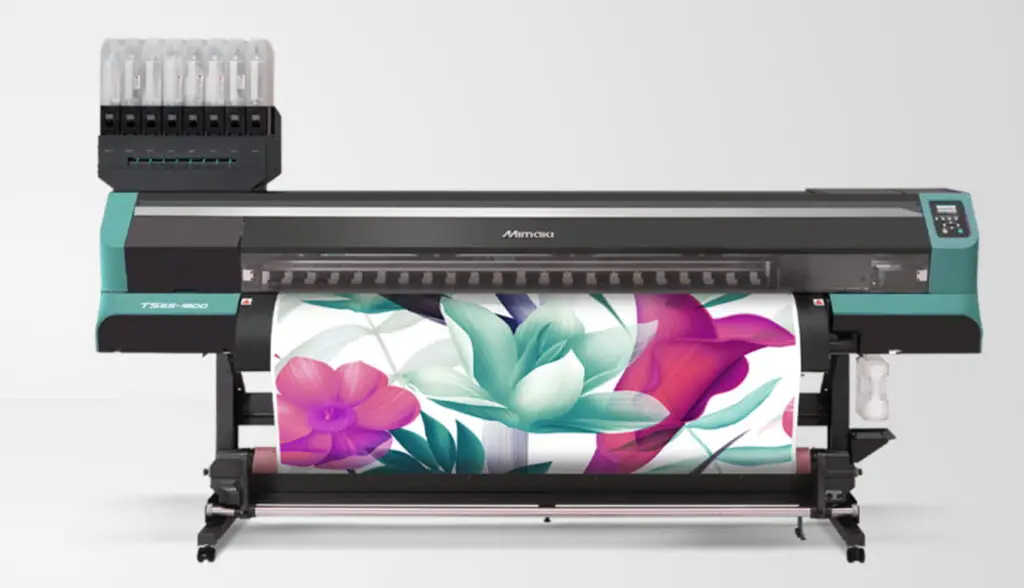

Do you see those gorgeous customized prints on fabrics, glassware, and other decorative items? These are made using the dye-sublimation printing technique. It is the most commonly preferred technique for fabric printing.
This procedure is quite unique but extremely easy to perform. Dye sublimation printers use heat to transfer dye onto a substrate. The process begins by printing a reversed image onto sublimation paper using special sublimation ink.
Heat and pressure transfer the image to a polyester fabric or other substrate. The heat and pressure from the press cause the dye to turn into a gas, at which point it permeates the fibers of the material and solidifies into the final image. The result is a vivid and permanent image that won’t fade or crack over time.
Pros
- Produces appealing and long-lasting prints.
- Easy to perform.
- Can print a wide range of customized designs.
Cons
- The process takes some time.
- Only compatible with special sublimation paper and sublimation inks.
Reactive Printing
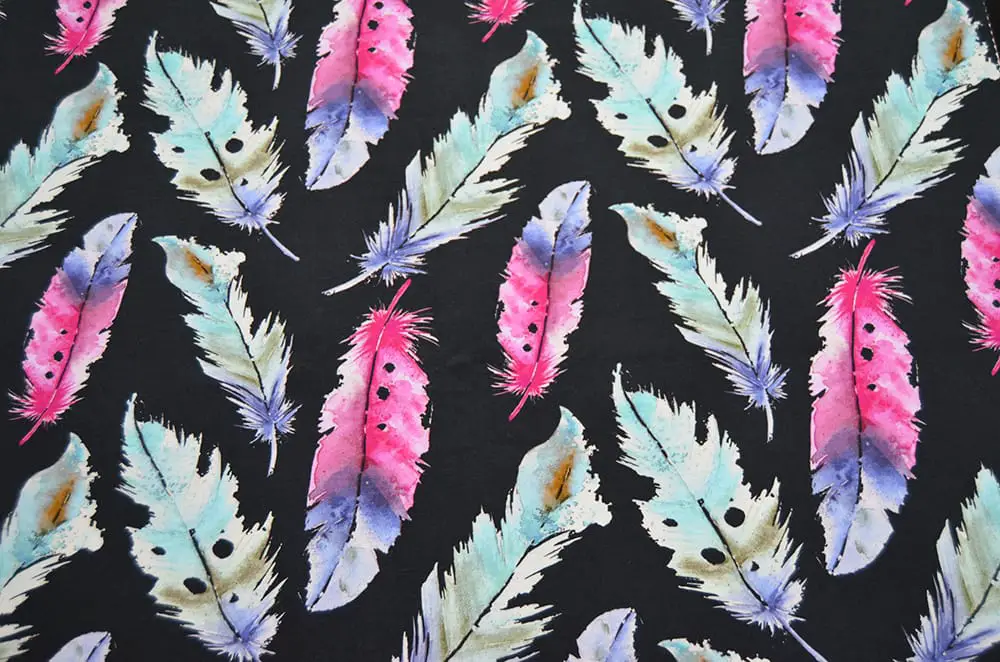

Another great method of textile printing in which the dye reacts chemically with the fibers of the fabric to create a permanent bond is reactive printing.
In this process, the design is printed onto the fabric using special reactive dyes. The dyes are then fixed onto the fabric via steaming or boiling. This printing type is well-known for producing vibrant and bright colors.
The most common application of reactive printing is on cellulosic fibers and cotton fabric. The process is also known for its eco-friendly as it utilizes water as the main solvent. Furthermore, the dye directly binds with fibers, reducing water and chemical waste throughout the procedure.
Pros
- Prints produced are resistant to fading and color bleeding.
- Eco-friendly process since no chemical-based solvent is used.
- Extremely durable prints.
Cons
- This multi-step complex process is challenging to master.
- Can fade over time with repeated washing.
- Reactive dyes are available in a limited range of colors.
Pigment Printing
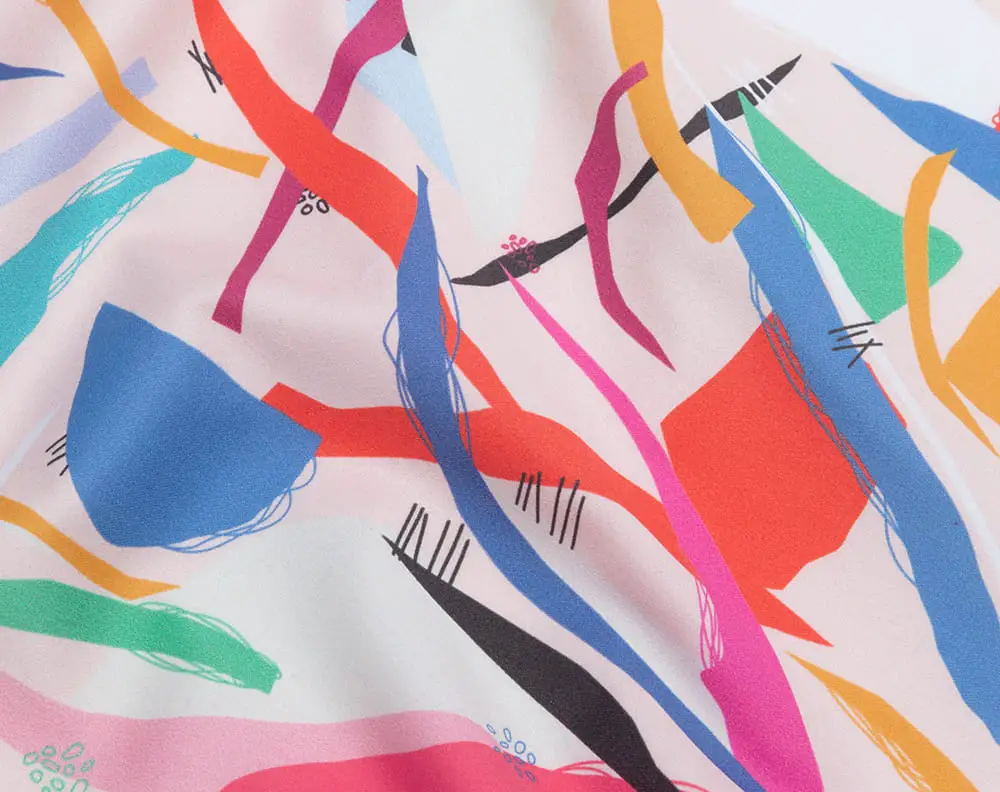

As mentioned earlier, it is a textile printing type and is mainly used in the fashion and home textile industries. Pigment printing creates the best designs on a wide variety of fabrics, including cotton, linen, rayon, and synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, and spandex.
The process works by using pigments suspended in a binder to create a print on fabric. In this technique, the design is printed onto the fabric using special pigment ink.
The pigment inks are insoluble color particles that are suspended in a liquid medium, such as water or a polymer.
Once it is printed on the fabric, it is then heated or treated with chemicals to cause the binder to evaporate, leaving the pigments behind on the fabric.
The pigments then bond with the fibers of the fabric to create a permanent print. In the end, the results are sharp, clear, and fabulous prints.
Pros
- Creates permanent and bright prints.
- Doesn’t require high-end machinery hence, less expensive.
- Amazing printing speed.
Cons
- Creates a coating on the fabric that is prone to tear.
- Pigment ink doesn’t embed with the fabric fibers.
Printing Techniques For Pottery And Utensils
Transfer Printing
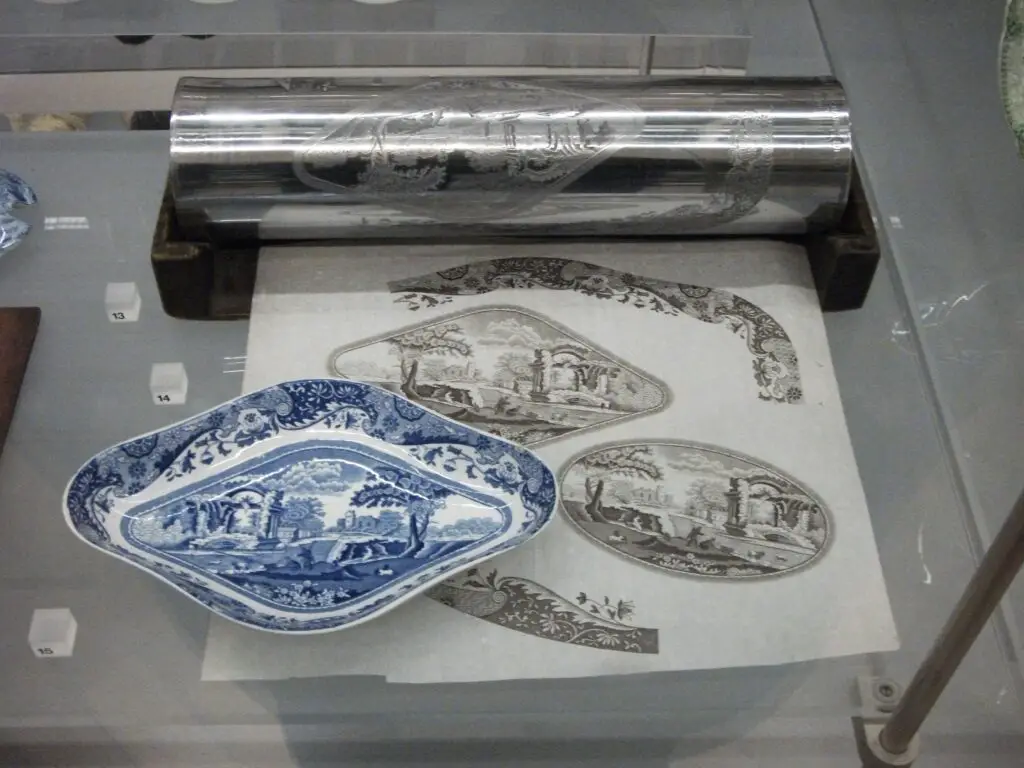

Typically, transfer printing is used to create logos or designs on curved surfaces. That said, these are best used for printing on pottery and utensils. Fortunately, this technique is compatible with porcelain, cotton, nylon, and polyester as well.
Transfer printing works by first printing a design onto special transfer paper using a digital printer or an inkjet printer. The design is printed in reverse, with the ink being printed onto the back of the transfer paper.
The fabric and transfer paper are then placed into a heat press, which applies heat and pressure to the paper. This causes the ink to transfer from the paper onto the fabric.
An easy approach to transfer ink on curved objects is by using a heat press with a curved platen. It lets you apply heat and pressure to the object evenly.
Once the pressing is done, the transfer paper is peeled off, leaving the design printed on the fabric. The overall process is pretty much similar to that of dye sublimation printing.
Pros
- The process doesn’t require special machinery.
- Can be done using a regular printer.
- Ideal for small businesses.
- No expert skills are required.
Cons
- Prone to peeling and cracking since prints create a film over the surface.
- Might not create very high-resolution prints.
Printing Techniques For Flyers, Magazines, Billboards, And Labels
LED UV Printing
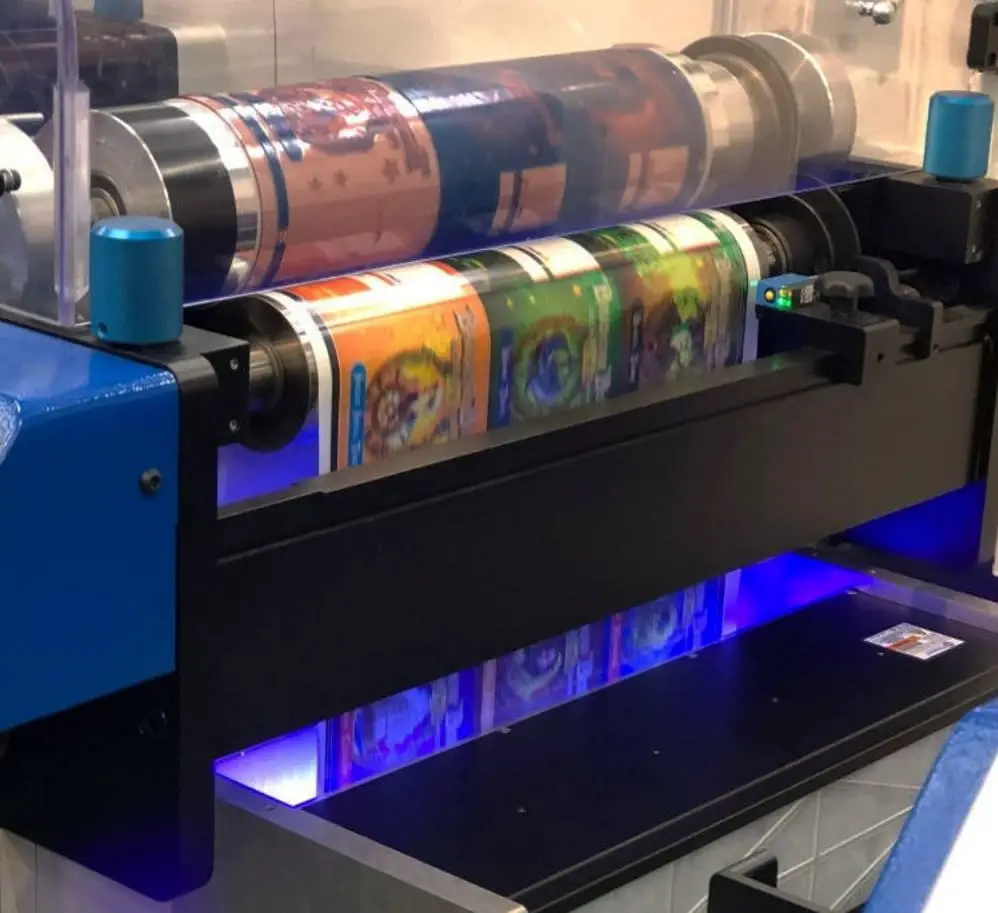

One of the great technological advancements is the invention of LED UV printing. This interesting process is perfect for creating labels, flyers, signs, brochures, etc.
LED UV printing uses ultraviolet (UV) light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to cure (dry and harden) ink as it is printed. It is a type of digital printing that works with UV-curable inks, which are activated and cured by the UV light emitted by the LED lamps hence, the name – LED UV printing.
A great thing about this technique is it’s a non-contact printing process. This means that the substrate does not come into contact with the printheads. As a result, there is minimal to no wear and tear on the printheads and no need for any special coatings or pretreatments on the substrate.
Pros
- Less time-consuming since inks cure instantly upon exposure to UV light.
- Extremely gorgeous prints with fine details and a wide color gamut.
- Smooth gradations even for complex designs.
- Non-contact printing ensures high longevity.
Cons
- Higher costs due to high-end machinery and curable inks.
- Limited substrate choice.
- The curing process can produce harmful ozone if there is improper ventilation.
Flexography Printing
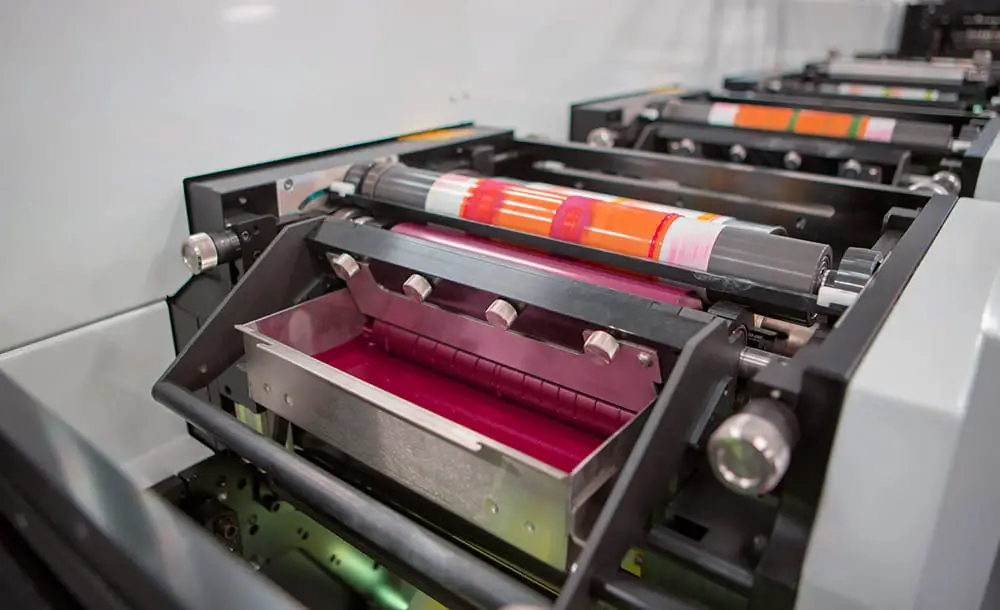

Often abbreviated as “flexo”, is a form of relief printing that uses a flexible plate made of rubber or photopolymer to transfer ink to the printing surface. It is a widely used printing process for packaging, labeling, and other types of commercial printing applications.
Flexography printing first makes a flexographic printing plate, which is a raised image of the design to be printed. The plate is made by creating a negative image of the design on a photographic film, which is then used to craft a mold of the image in rubber or photopolymer. The plate is then mounted on a plate cylinder on the flexographic press.
Ink is then applied to the plate through a metering roll, which evenly distributes the ink. The plate cylinder then rotates and comes in contact with a rubber blanket cylinder, which picks up the ink from the plate and transfers it to the substrate. As the substrate is passed through the press, the ink is pressed into the surface, creating the printed image.
Pros
- Able to print high-volume runs at fast speed.
- Compatible with a wide range of substrates including uneven surfaces.
- Cost-effective printing technique.
Cons
- Unable to produce high-resolution images with fine details.
- Limited color range.
Gravure Printing
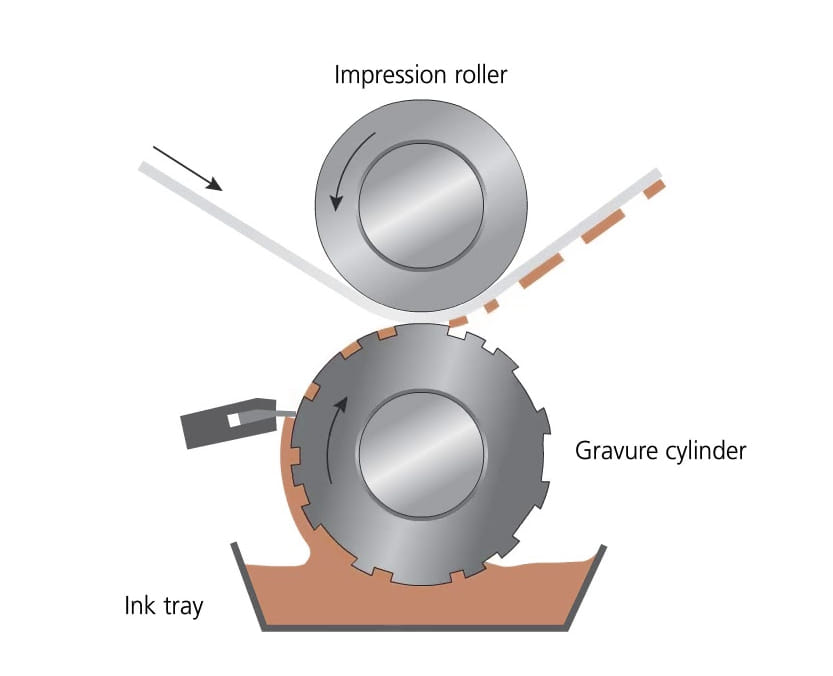
It is a type of intaglio printing that uses a rotogravure press to transfer ink from an engraved cylinder onto the printing surface. Gravure printing is a common process used for packaging, newspapers, magazines, etc.
First, the image to be printed is prepared and sent to the printer. A metal cylinder, typically made of copper or steel, is engraved with a negative image of the design. The cylinder is engraved using a chemical etching process or a laser engraving process. The engraved area will hold the ink, while the non-engraved areas will not.
The engraved cylinder is then mounted on a rotogravure press, and coated with a layer of ink. Then, the substrate, typically paper, film, or other materials, is then fed through the press and comes into contact with the engraved cylinder.
As the cylinder rotates, the ink is transferred from the cylinder onto the substrate, creating the printed image. The substrate is then passed through the press, the ink is transferred from the cylinder onto the surface, creating the print.
Unfortunately, this method is gradually losing its spot in the printing market. Flexo is taking over for printing packaging and labels. Whereas, offset litho is considered a better alternative for publication printing.
Pros
- Prints amazingly on thin films and substrates.
- Excellent for producing colorful images.
- The prints last exceptionally long.
Cons
- Small texts might appear jagged.
- An overall expensive process.
- Requires frequent maintenance.
Large Format Printing
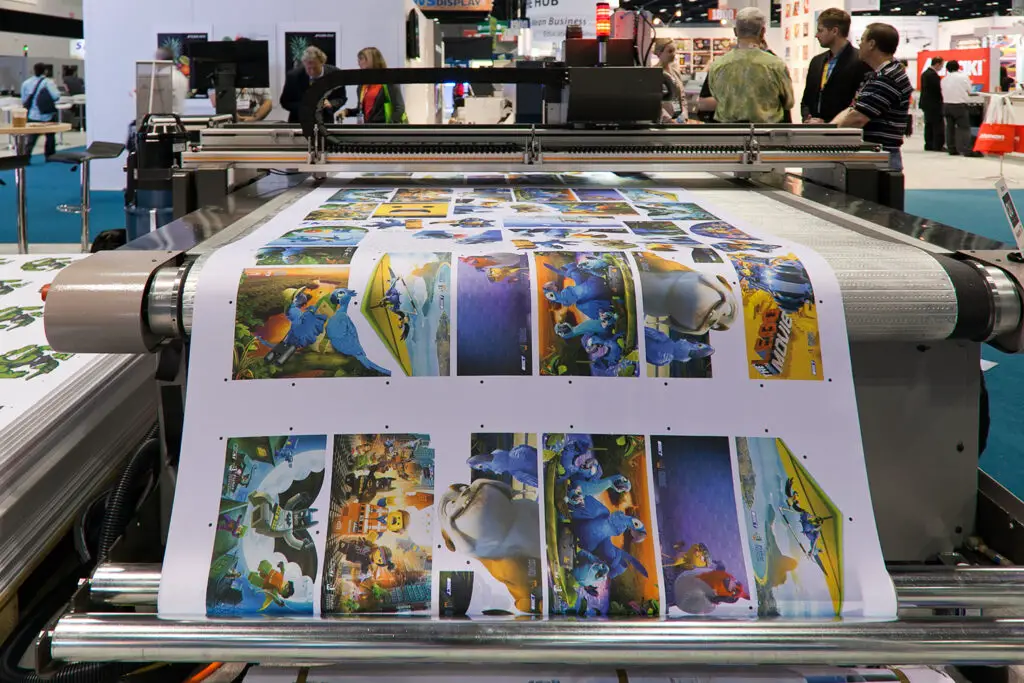

As referred to by the name, large-format printing is done on large-sized media, such as posters, banners, trade show graphics, wallpaper, murals, backdrops, and more. The “large format” indicates the size of the media and not the size of the printer. These prints can be as small as 2 feet and as large as 150 feet or more.
For this technique, wide-format printers are used that are designed to handle larger rolls of media than standard printers. These printers use a variety of print technologies such as inkjet, sublimation, and UV-cured printing.
There are two common types of large-format printing i.e., flatbed printing and roll-to-roll printing.
- Flatbed printing – It uses a flatbed as the printing surface, usually for rigid materials like acrylic, foam board, aluminum, glass, etc.
- Roll-to-roll printing – It uses a roll of flexible material as the printing surface, usually for fabrics, vinyl, and other flexible materials.
Large-format printing is a common technique performed regularly in a variety of industries, including advertising, retail, architecture, and event planning.
Pros
- Ideal for producing high-end prints on a massive-sized substrate.
- Creates less waste compared to other printing types.
- Relatively fast.
Cons
- Requires skilled staff to manage to print.
- Very specific for its purpose.
Letterpress Printing
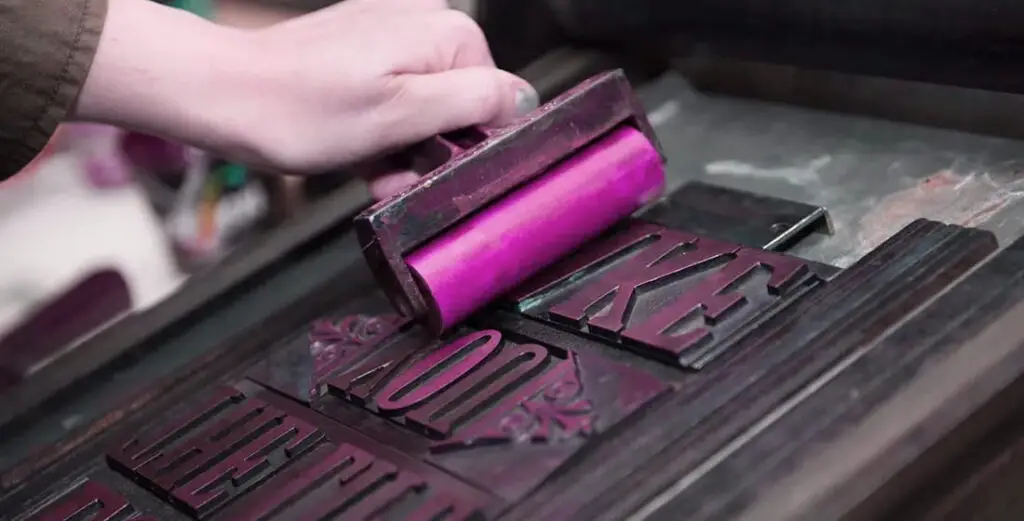

Letterpress printing is one of the old methods that has been revolutionized into an advanced printing technique. It is a brilliant choice for printing top-end business cards, invitations, packaging, labels, books, etc.
It is also a form of relief printing, similar to flexography, and letterpress printing is considered an art form. It uses a press with raised letters or images to transfer ink onto the printing surface.
The text or design to be printed is first prepared and set in metal or wooden type. This includes selecting the typeface, size, and layout of the text or design. The type is then carefully arranged on a press bed in the desired layout, with the raised letters facing upwards.
Finally, the press bed is then pressed against the printing surface, such as paper or cardstock, transferring the ink from the type to the surface to create the printed image. The final product is then cut to the desired size and shape.
Pros
- Superb for printing short runs.
- Creates a unique yet appealing print on every type of compatible substrate.
- Works on uneven surfaces as well.
Cons
- Challenging to print images.
- Labor-intensive process.
- Needs skills due to high complexity.
Now that you know the different printing types and techniques alongside their working and applications, choose the one that matches your purpose of use and requirements. Happy printing!





